Kia ora Toiere whānau We’re excited to invite you to a special webinar with Paul…
AI Workshop with AI Sandbox
🧠 Rātā Workshop #4 – AI Education and Empowerment
Supported by the Rātā Foundation
Delivered by Nelson AI Sandbox
A foundational session introducing non-profit and community organisations to Artificial Intelligence (AI) — focusing on understanding the technology, using it safely, and planning for responsible adoption in Aotearoa New Zealand.
👥 Speakers
Sloane Bayley – Programs Manager, Nelson AI Sandbox
AI enthusiast, with a focus on supporting the non-profit sector.
J Norness – Fractional Chief Marketing & AI Officer
Director and advisor helping organisations use AI strategically and safely.
🎯 Workshop Overview
The session covered:
-
Introduction to Generative AI
-
Privacy, Safety, and Security
-
Practical Tool Demonstrations
-
Sustainability and AI Impact
-
Example Case: SOLE (a fictional NFP)
-
Creating and Implementing an AI Policy
-
Understanding AI Agents and Tools
-
Planning for Organisational AI Use
🌏 AI Context in Aotearoa
-
New Zealand currently lacks strong AI regulation, creating risks around data scraping and privacy (e.g., Meta using NZ/AU user data for AI training).
-
The non-profit sector is adopting AI faster but often without governance frameworks in place.
Key Stats (Infoxchange AU & NZ, 2024):
-
76% of organisations use generative AI tools (up 52% in a year).
-
Only 33% are actively investing across the organisation.
-
20% hesitate due to lack of understanding; 13% are concerned about privacy or data sovereignty.
-
89% have no AI policy in place.
-
In Te Tauihu, 75% of NFPs have no AI policy.
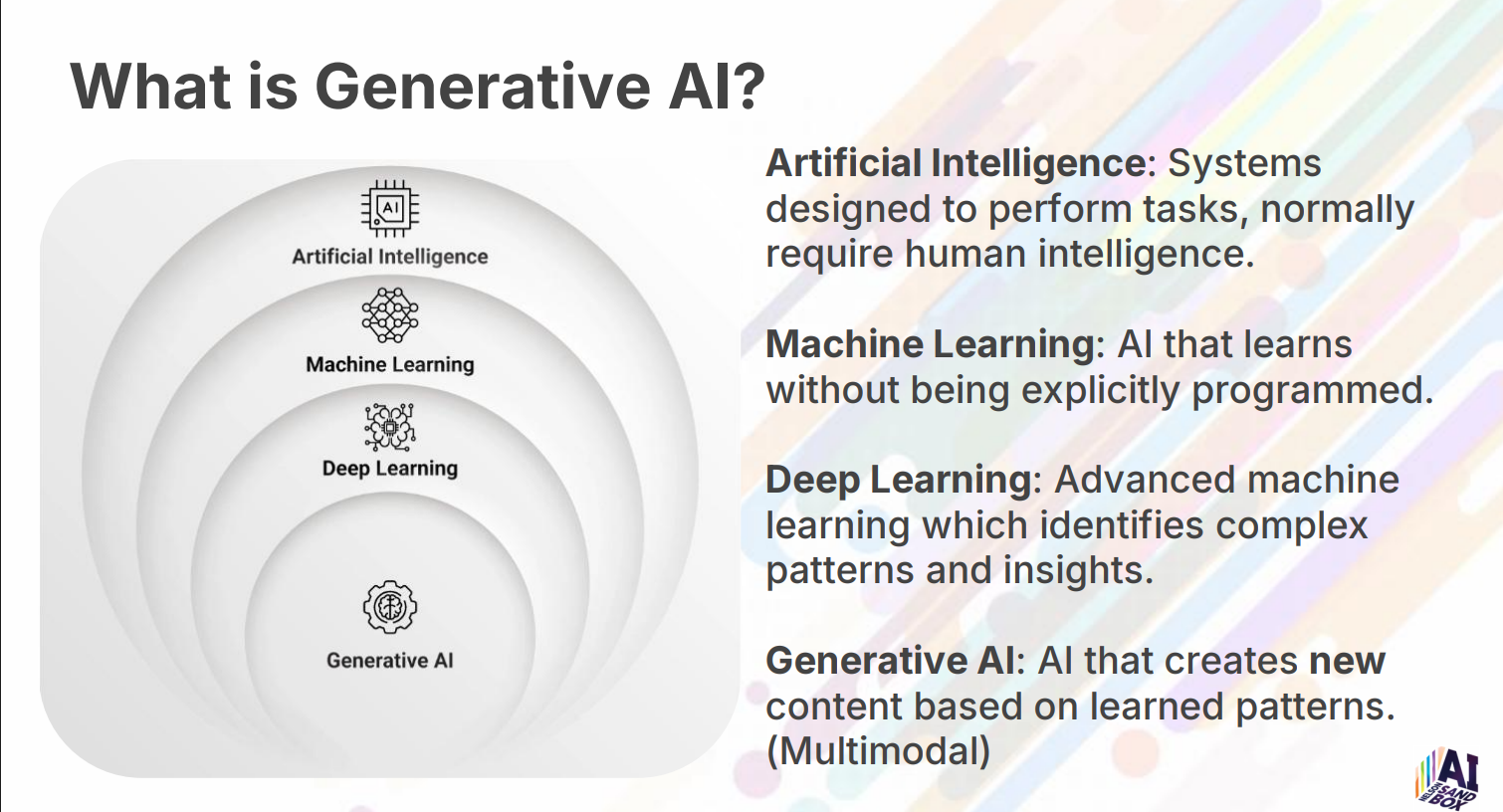
🧩 Understanding Generative AI
-
Artificial Intelligence = machines performing human-like tasks.
-
Machine Learning (ML) = systems that learn from data.
-
Deep Learning = advanced ML that identifies complex patterns.
-
Generative AI = creates new content (text, images, video, music, code).
-
Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT are trained to predict language patterns — they don’t “know”, they predict.
💡 Four Ways to Think About Generative AI
-
Superpower: Extend and enhance human ability.
-
Many Interns: Multiple assistants for different tasks.
-
Thought Partner: Helps test, clarify, and refine ideas — not replace thinking.
-
Autonomous Interns: AI agents that can plan, decide, and act toward a goal.
🔐 Privacy, Safety & Security
AI tools come with risks:
-
Bias (how models were trained)
-
Hallucination (incorrect or made-up info)
-
Privacy leaks (data exposure or misuse)
-
Cyber risks (e.g., deepfakes, malicious code injection)
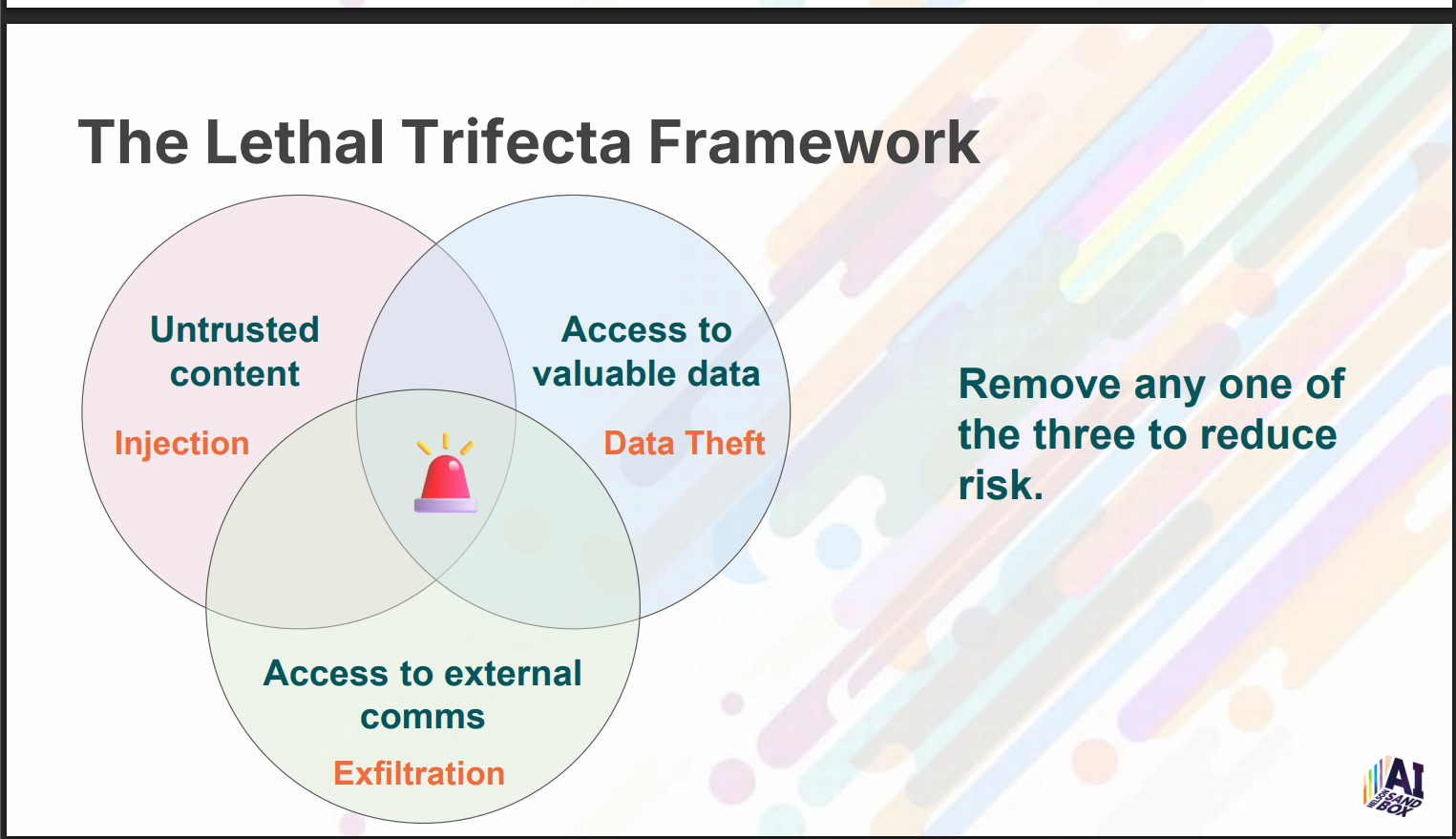
Frameworks introduced:
-
Lethal Trifecta: Risk arises when systems have (1) untrusted content, (2) access to valuable data, and (3) external communications. Remove one to reduce risk.
-
Three Safety Tiers:
-
Open (low risk) – marketing, public info
-
Controlled (medium) – internal reports
-
Locked (high) – payroll, IP, HR data
-
Golden rule:
➡️ Human > AI > Human — every output should be checked by a person.
🌿 AI Sustainability
AI requires large energy and water use (Amazon used 105 billion gallons in 2021).
Challenges: computing power, resource extraction, and rebound effects.
Solutions:
-
Measure and manage energy impact.
-
Use smaller, specialised models.
-
Support clean energy and efficient infrastructure.
🧦 Case Study: SOLE (Society of Left Enthusiasts – Nelson & Tasman)
A fictional non-profit created to demonstrate AI in practice.
SOLE’s mission: “Making Lefts Right” – investigating the disappearance of left socks.
Used to show:
-
How to generate branding, jingles, and visuals.
-
How to build custom GPTs to handle policies, minutes, and agendas.
-
How NFPs can safely test AI tools.
💬 Prompting Basics
Prompt = what you tell AI to do.
Clearer prompts → better results.
CARE Framework:
-
Context – what’s happening?
-
Action – what task to do?
-
Role – who should AI act as?
-
Expectation – what output do you want?
Examples:
“Summarise this policy for a board meeting.”
“Act as a grants officer and rewrite this in plain English.”
⚙️ Custom GPTs & Agents
Custom GPTs:
-
Personalised versions of ChatGPT tailored to an organisation’s tone, data, and needs.
-
Example: SOLE Virtual Director — stores minutes, creates agendas, answers policy questions.
Agents:
-
AI systems that act autonomously.
-
Can learn, plan, or collaborate with other agents.
-
Used for chatbots, scheduling, website optimisation, data analysis, etc.
🛠️ Useful AI Tools
-
Fireflies / Otter AI: meeting notes and transcription
-
SmythOS / N8N: build agents without code
-
Vapi / Bland AI: voice and phone-based AI
-
Synthesia / Leonardo / Sora: create avatars, images, and video
-
Infoxchange.org: guidance for NFP AI adoption
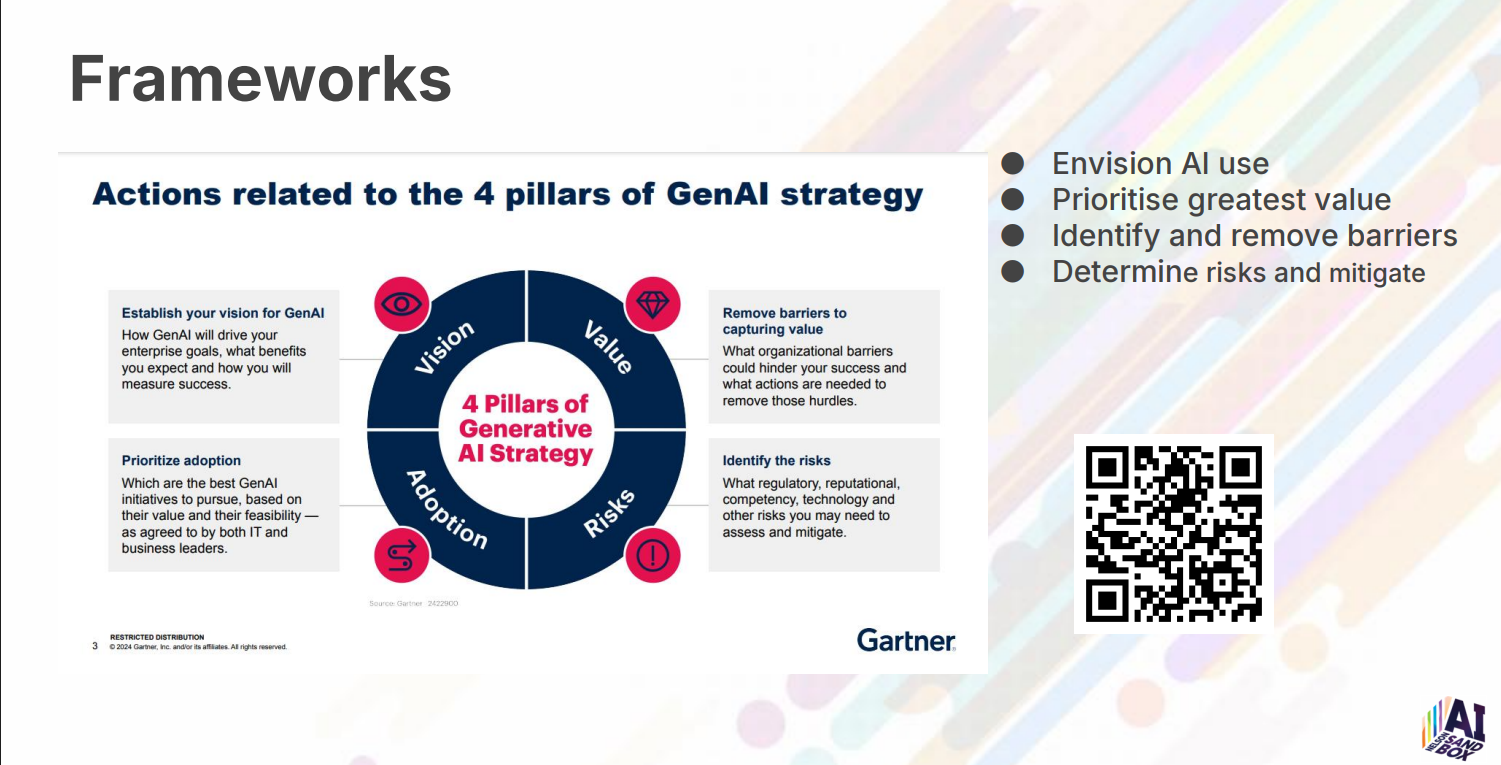
🧭 Strategic AI Planning
Use frameworks to plan and prioritise:
-
Envision where AI adds value
-
Prioritise high-impact, low-complexity projects
-
Identify barriers and risks
-
Mitigate before rollout
Next Steps for NFPs:
-
Identify AI Champions.
-
Develop an AI Policy and Tool Register.
-
Run AI training sessions.
-
Improve data quality and governance.
-
Plan integration and maintenance of tools.
📍 Key Takeaways
-
AI is transforming all sectors — including non-profits.
-
Ethical use, governance, and Māori data sovereignty are essential.
-
Start small: experiment safely, train your team, and document your approach.
-
Policies and human oversight protect people, data, and trust